编写程序main,在程序main中调用lib.so中的myprintf函数。
main.cc
//main.cc
#include <iostream>
#include <dlfcn.h> //dlopen等函数需要的头文件
int main(int argc,char* argv[])
{
void* dlp = dlopen("./lib.so",RTLD_NOW);
if (dlp)
{
std::cout << "dlopen is OK!" << std::endl;
typedef void (*pf_myprintf)(const char* str);
pf_myprintf myprintf = (pf_myprintf)dlsym(dlp,"myprintf");
if (myprintf)
{
char txtbuf[100];
std::cin.get(txtbuf,100);
myprintf(txtbuf);
}
else
{
std::cout << "dlsym is failed!" << std::endl;
}
}
else
{
std::cout << "dlopen is failed!" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
lib.cc
//lib.cc
#include <iostream>
extern "C"__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void myprintf(const char* str)
{
std::cout << "-----myprintf begin-----" << std::endl;
std::cout << str << std::endl;
std::cout << "------myprintf end------" << std::endl;
}
extern "C" void test_export1()
{
std::cout << "-----test_export-----" << std::endl;
}
__attribute__((visibility("default"))) void test_export2()
{
std::cout << "-----test_export-----" << std::endl;
}
makefile
#main lib makefile main:main.cc g++ main.cc -o main -ldl lib:lib.cc g++ -o lib.so lib.cc -shared -fPIC -fvisibility=hidden clean: -rm main *.so
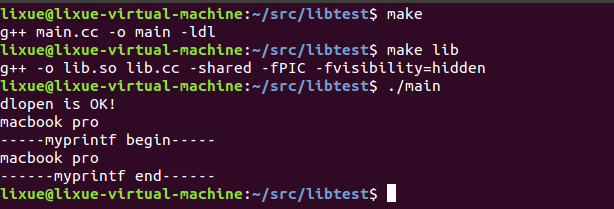
使用make来编译生成主调程序,使用make lib来生成库程序lib.so,而后执行main即可调用动态库中的函数,如图1所示。
下面我们看看lib.cc中的三个函数都哪个导出了,使用命令readelf -s lib.so,结果如图2所示。
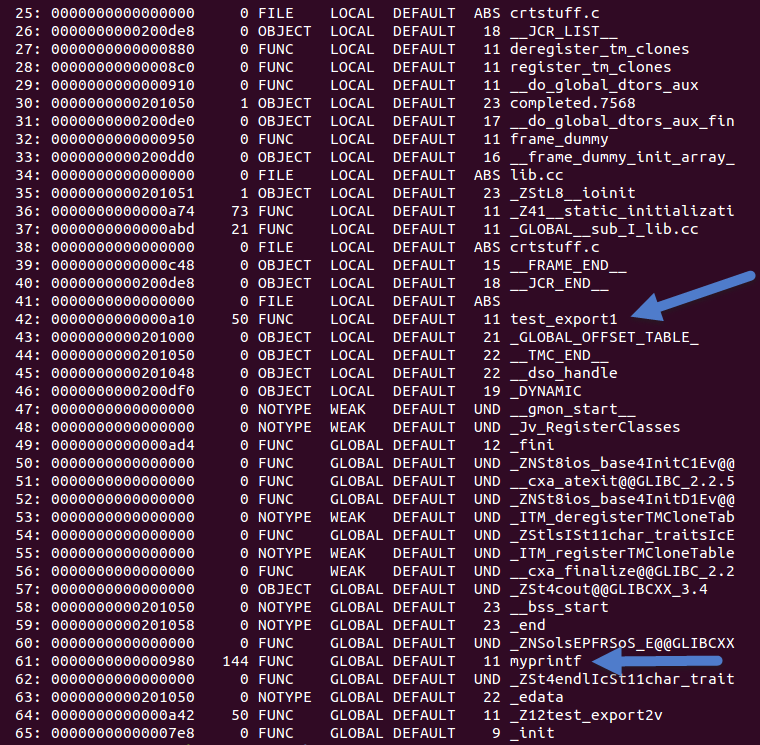
可以看到,三个函数只有test_export2没有被导出,也只有这个函数没有用extern "C"标注,另外,该函数使用了__attribute__((visibility("default")))。由此可以得出以下假设:
- 使用g++编译动态库,会导出具有
extern "C"标识的函数,在gcc中有效的__attribute__((visibility("default")))标识在g++中无效。原因可能是因为__attribute__是Linux C中特有的标识,在C++中很有可能没有作用。 - 另外从lib.so的导出符号表中可以看到一些C++形式的导出函数,所以一定是还有其它方法可以直接导出C++形式的函数。
发表回复